Power Ratio in dB
The Power ratios in dBIf P1 and P2 are powers expressed in watts, then one way to express their ratios is to simply say that P2 is x times that of P1. If P2 is 10 watts and P1 is 2.5 Watts we say that P2 is 4 times that of P1.
There are however instances where expressing the ratio in simple way does not convey the reality. Take the example of the sound. If you double the power output from the speaker you do not hear a sound whose intensity is “felt” doubled.
Engineers have defined another ratio to express the ratio of powers that expresses the reality more closely. They define the ratio of two powers in dB as follows
Power ratio in dB = 10 log10 (P1/P2)
Some examples help you understand and memorize the facts.
Example - An amplifier amplifies a power from 1 watts to 20 watts. Find the power gain in dB
Solution - Power gain in dB = 10 log10 (P1/P2)
= 10 log10 (20/1)
= 10 log10 (20)
=10 [log10 (10) + log10 (2)]
= 10[1+0.3010]
= 13.01 dB
Example - An amplifier amplifies an input signal by 4 dB. If the input power is 2 watts, what is the output power.
Solution – Power gain in dB = 10 log10 (P1/P2)
Let us express power gain in dB by x.
x = 10 log10 (P1/P2)
Here x = 4 dB
P2 = 2 Watts
P1/P2 = 10x/10
P1/2 = 104/10
P1 = 5.023 Watts
Notice that if P1 is less than P2, the power ratio is negative. If a signal propagates and is get attenuated the power gain is negative in dB. The more negative is the number, greater is the attenuation.
Example A 10 watt signal propagates down a cable and gets attenuated because of the losses. Find the loss in dB if the received signal is 3 watts.
Solution - Power gain in dB = 10 log10(P1/P2)
= 10 log10 (3/10)
= -5.2 dB
Expression of Power in Absolute Unit - dBm
dBm is a unit for expressing absolute power. It can be thought of expressing the power in dB with respect to 1 milli watt.
Power in dBm = 10 log10 (P1/1 milliwatt)
The chart below shows common dBm to watts conversions.
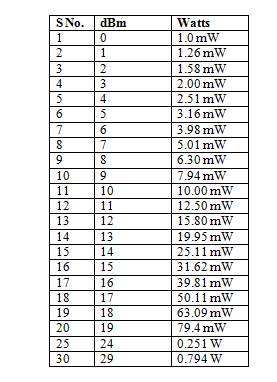
You will notice that when the power doubles, there dBm value increases by 3. Engineers say express this as there is a 3 dB gain every time power doubles.
Example - Find the power in dBm corresponding to 1 watt of power.
Solution - Power in dBm = 10 log10 (P1/1 milliwatt)
= 10 log10 (1 Watt /1 milliwatt)
= 10 log10 (1/0.001)
=10 log10 (1000)
= 30 dBm
Example - Most radio receivers perform satisfactorily if the power received is above -87 dBm. Find the value of this power level in watts.
Solution - Power in dBm = 10 log10 (P1/1 milliwatt)
Here, Power in dBm = -87
Therefore,
-87 = 10 log10 (P1/1 milliwatt)
P1 = 0.001 * 10-8.7
= 1.995 * 10-12 Watts
The -87 dBm is equivalent to 1.995 pico watts.
Power gain in nepers
Nepers is another unit to express the power ratio. It is defined as
Power ratio in nepers = ½ ln (P1/P2) [9 11]
We can find the ratio of the powers expressed in dB and nepers as follows.
Let x is the power ratio expressed in nepers and y is the power ratio expressed in dB.
x = ½ ln (P1/P2)
y = 20 log10 (P1/P2)
Dividing the two equations we get
y/x = 20 log10 (P1/P2)/ ln (P1/P2)
= 20 log10 e
= 8.685
1 nepers is therefore equal to 20*log10 e dB or 8.685 dB
In high speed signal integrity, engineers often talk about the losses in the signal in terms of dB instead of watts. We should be able to form an idea of interpretation of the dB losses.
Power Ratio in dB in terms of voltage ratio.
Let us assume that two circuits have impedances z1 and z2 respectively. If v1 is the voltage across the impedance z1 of first circuit and v2 the voltage across the impedance z2 on the second circuit, then the Power ratio is expressed as
Power ratio in dB = 10 log10 [(v12/ z1)/ (v12/ z2)]
The z1 and z2 are the magnitudes of the impedances of the two circuits. If the impedances of the two circuits are same, then the Power ratio can be expressed as,
Power ratio in dB = 20 log10 [v1/ v1]
Voltage Ratio in dB
The voltage ratio in dB is defined as
Voltage ratio in dB = 20 log10 (V1/V2)
Expression of Voltage in Absolute Unit – dBmV
Similar to dBm for power, there is a unit to express the voltage in dBmV. It represents the voltage level with respect to 1 millivolt.
Voltage level in dBmV = 20 log10 (V1/1 milliVolt)
We should note that the expression for dBmV applies for rms value as well as peak to peak value. We should specifically mention that it is a peak to peak value if it is so.
Expression of Voltage in Absolute Unit – dBµV
dBµV is referenced to 1µV and similar to the absolute expressions above it is given by
Voltage level in dBµV = 20 log10 (V1/1µV)
dBµV is often used for the RF receiver sides calculation where the power levels are very small.
Example 9 11 - Find the voltage level in dBmV corresponding to 10V.
Solution - Voltage level in dBmV = 20 log10 (V1/1 milliVolt)
Substituting V1 = 10 V
dBmV = 20 log10 (10/10-3)
= 20 log10 (10+4)
= 80
10 Volts will correspond to 60 dBmV.
Example Find the voltage level in corresponding to 10 dBmV.
Solution Voltage level in dBmV = 20 log10 (V1/1 mV)
Or V1 = 10-310dBmV/20
Substituting dBmV = 10
V1 = 10-31010/20
= 3.16 mV
10 dBmV will correspond to 3.16 mV.
Example - The PCB trace loss was reported to be 0.28 dB at 1 GHz. If the incident voltage was 3.3V fid the voltage level at the end of the trace.
Solution The loss in dB is given by
Voltage ratio in dB = 20 log10 (V1/V2)
V2 = V1/10dB/20
= 3.3V / 1.0327
= 3.195 V
Previous - Transmission Line Losses Next - Skin Effect