Capacitance and Capacitor
CHAPTER 44 Capacitance and Capacitor
Before understanding capacitance and capacitor, let us understand the basic concept of and voltage.
Think of the presence of an electric field. The electric field can be created by the presence of an electric charge. If there is a very small charge q, the electric field starts from the charge and points outwards away from the charge.

Figure 4 1 - Electric lines of forces from a single point charge.
If we place another positive charge q in this field, it will be repelled by the electric field. If we want to make the positive charge move towards the charge, against the electric field, we will have to do some work against the electric field. If W is the amount of work done in moving a charge q between the two points, the potential difference between these two points is give by.
V = W /Q [4-1]
The potential difference between two points is defined as the work done in moving a unit positive charge between these points.
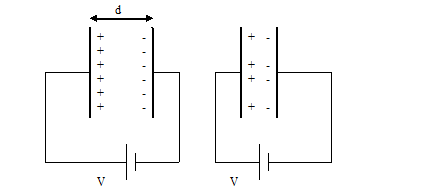
Figure 4 2 - If we make the plates come closer, the charge accumulated on them decreases
To understand concept of capacitance, consider two parallel plates, the plates being at distance d apart. The structure is connected to a voltage source of voltage V. As a result of this, electrons start to flow from the negative end of the voltage source to the right side of the parallel plate. When the electrons are accumulated on the right side of the plate, they repel the electrons present on the left side plate. The electrons on the left plate start departing from the plate. This results in the left plate being positively charged. The electron accumulation on the right plate keeps growing. At the same time the electrons on the left plate keeps departing. With the left plate positively charged and the right plate negatively charged, there is a electric field between the plates. This field prevents further charge accumulation. There comes an equilibrium point when there is no increase in charge accumulation.
If q is the charge accumulated on the capacitor when a voltage V is applied across it, the capacitance is given by
C = q/V
The capacitance of a capacitor is therefore defined as the charge accumulated on it when 1 V of potential is applied across it.
If the separation between the two plates of the capacitor is decreased, the charge required to maintain a voltage V across it increases. The capacitance therefore, increases.
Parasitics of SMT Resistor Next - Parallel Plate Capacitor