Impedance of Capacitor
CHAPTER 44.3 Impedance of a Capacitor
The impedance of a capacitor is given by
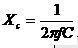
where ,
f = frequency
C = Capacitance of the Capacitor,
Xc = Impedance of the Capacitor
In signal integrity area, decoupling capacitors are used to provide low impedance path to ac signals between power and ground planes. What do we mean by providing a low impedance ac path between power and ground? We want to keep the power distribution system free from any noise over it. We want only DC signal over it. If some noise does come somehow on the power rail, then we should have a device which will make this ac signal flow to ground through this device instead of finding its way to the other components on the power supply rail. A capacitor is such a device.
At low frequency or for the DC signals, the Capacitor appear open to the low frequency or to the DC signal. There is no function of the capacitor here. If our power signal would have been a pure DC signal under all DC conditions, there is no use of decoupling capacitors. They should all be removed. Practically however, there are a number of noise sources which enter into the power rail. If such a case happens, there is a low impedance between these noise source and the ground formed by these capacitors. This results in the noise source grounded by the capacitors.
4.3 Capacitance in a Signal Path
While the capacitance between the power and the ground signal are beneficial, the capacitance between the high speed signal path, more often than not, distort the signal. This capacitance can be formed by a via, a thick trace at card edge connector, SMD pad, BGA pad or a test point.
Previous - Parallel Plate Capacitor Next - Real Capacitor