Effect of Apertures in Shielding
An ideal shield is a Faraday enclosure with not openings, holes or discontinuities. Practically, however, the enclosures need apertures or holes for connectors, heat ventilations or buttons. The apertures reduce the effectiveness of the shield.
The leakage from these apertures depends upon the maximum length of the opening. The slot becomes an efficient radiator if its length is ¼ th of the wavelength or larger. The slot will be an inefficient radiator if the length is 1/100 th of the wavelength.
Practically, it will mean that you will find the frequencies of the peaks of the radiation spectrum. Find the highest frequencies in your emission spectrum. Keep the slots less that 1/00 th of the wavelength of the highest frequency elements.
Example - The emission spectrum shows 200 MHz peaks. There are no major spectral peaks beyond 200 MHz. A metallic enclosure is design to shield the radiation. Find the maximum aperture length applying 1/100 th wavelength rule.
Solution
The wavelength corresponding to 100 MHz is given by
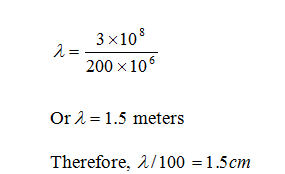
It will be better if we restrict the length of the opening to 1.5 cm. The lower the better.
Previous Next